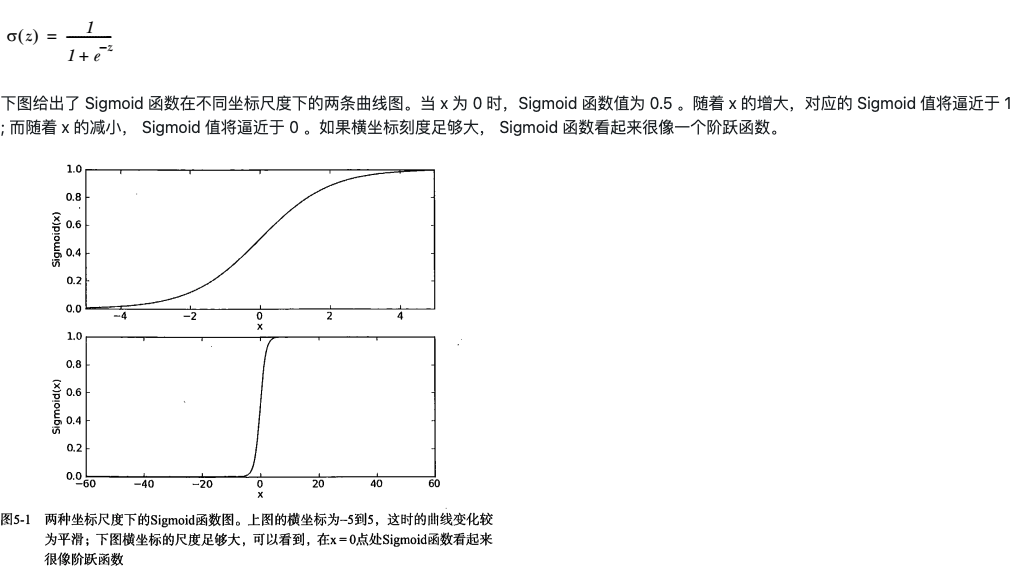
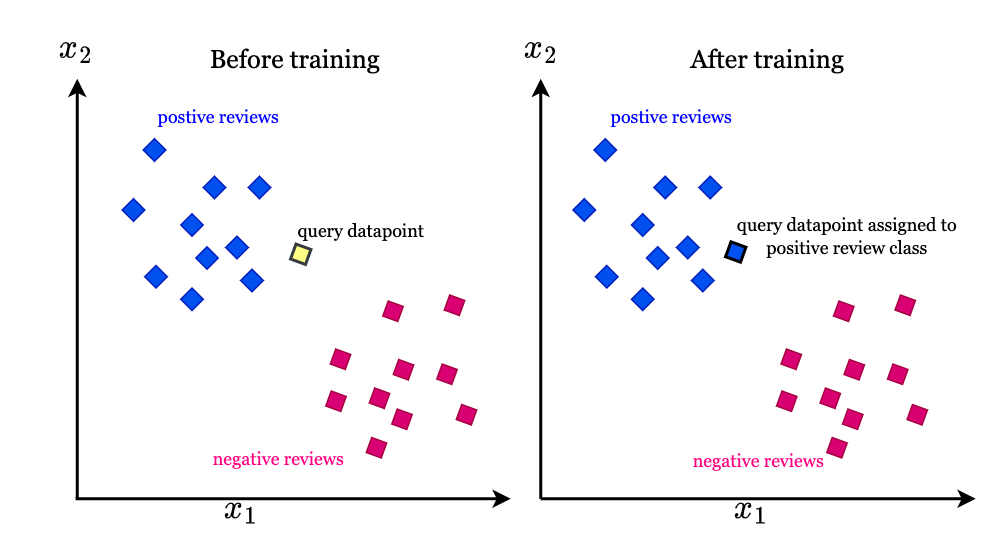
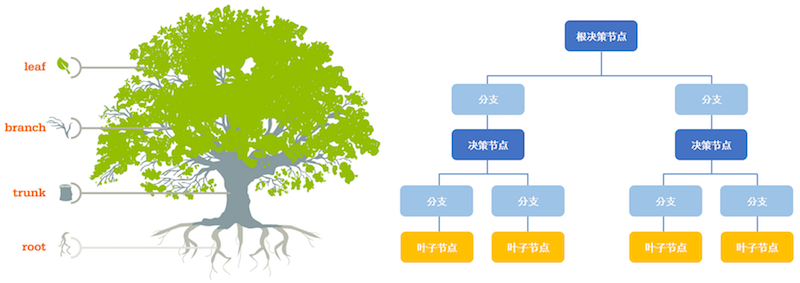
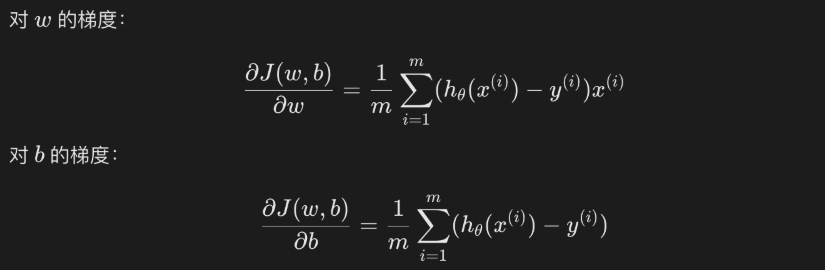1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
| import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data[0:100]
Y = iris.target[0:100]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01, num_iterations=1000):
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.num_iterations = num_iterations
self.weights = None
self.bias = None
def sigmoid(self, z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def initialize_parameters(self, n_features):
self.weights = np.zeros(n_features)
self.bias = 0
def compute_cost(self, X, y, weights, bias):
m = X.shape[0]
z = np.dot(X, weights) + bias
predictions = self.sigmoid(z)
cost = (-1/m) * np.sum(y * np.log(predictions) + (1-y) * np.log(1-predictions))
return cost
def fit(self, X, y):
m, n_features = X.shape
self.initialize_parameters(n_features)
costs = []
for i in range(self.num_iterations):
z = np.dot(X, self.weights) + self.bias
predictions = self.sigmoid(z)
dw = (1/m) * np.dot(X.T, (predictions - y))
db = (1/m) * np.sum(predictions - y)
self.weights -= self.learning_rate * dw
self.bias -= self.learning_rate * db
cost = self.compute_cost(X, y, self.weights, self.bias)
costs.append(cost)
print(f"Iteration {i}, Cost: {cost:.6f}")
return costs
def predict(self, X):
z = np.dot(X, self.weights) + self.bias
predictions = self.sigmoid(z)
return (predictions >= 0.5).astype(int)
def score(self, X, y):
predictions = self.predict(X)
accuracy = np.mean(predictions == y)
return accuracy
model = LogisticRegression(learning_rate=0.1, num_iterations=10)
costs = model.fit(X_train, y_train)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(range(len(costs)), costs, 'b-', label='Training Loss')
plt.xlabel('Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.title('Training Loss Curve')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
train_accuracy = model.score(X_train, y_train)
test_accuracy = model.score(X_test, y_test)
print(f"\n训练集准确率: {train_accuracy:.4f}")
print(f"测试集准确率: {test_accuracy:.4f}")
|